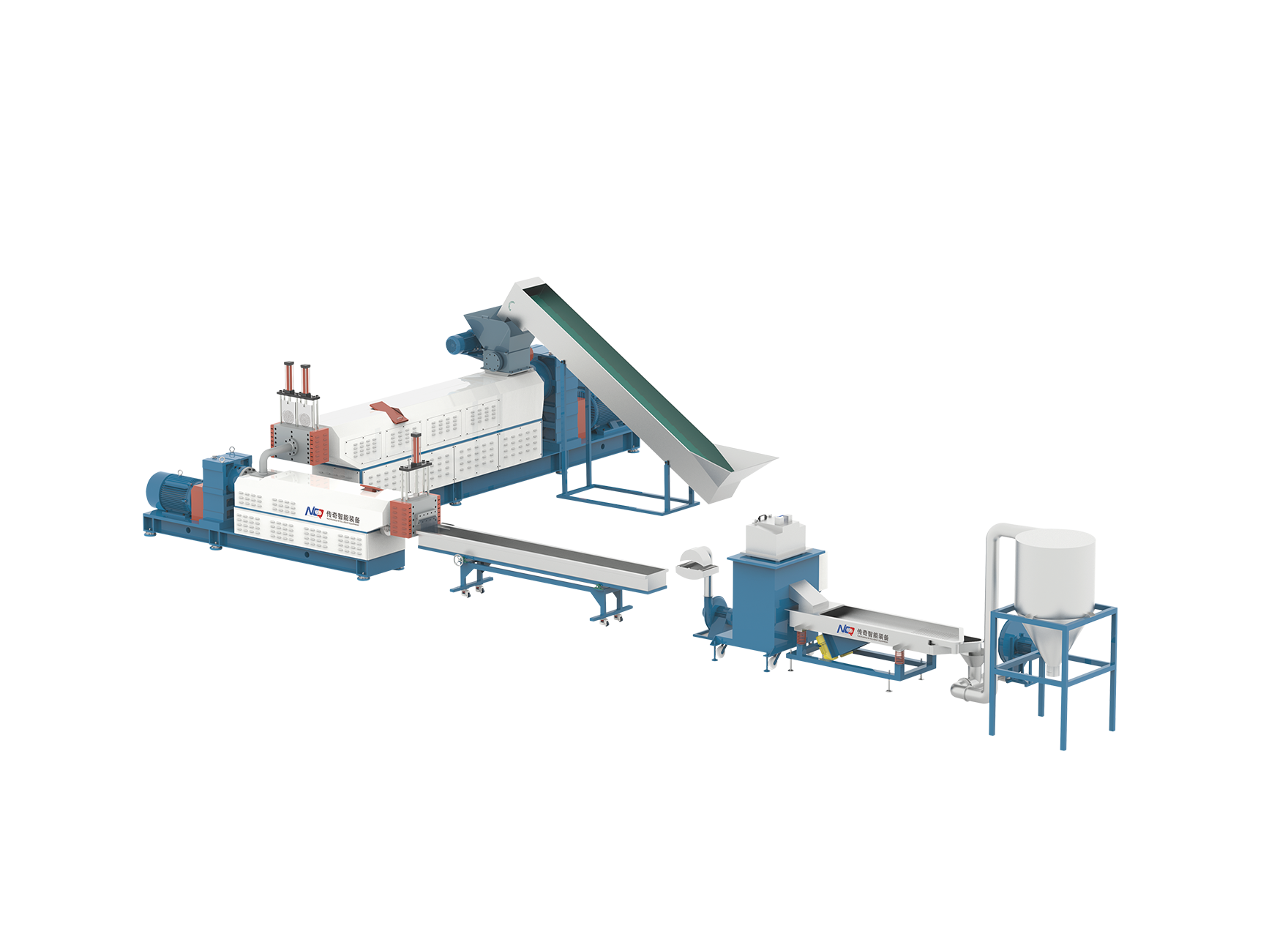
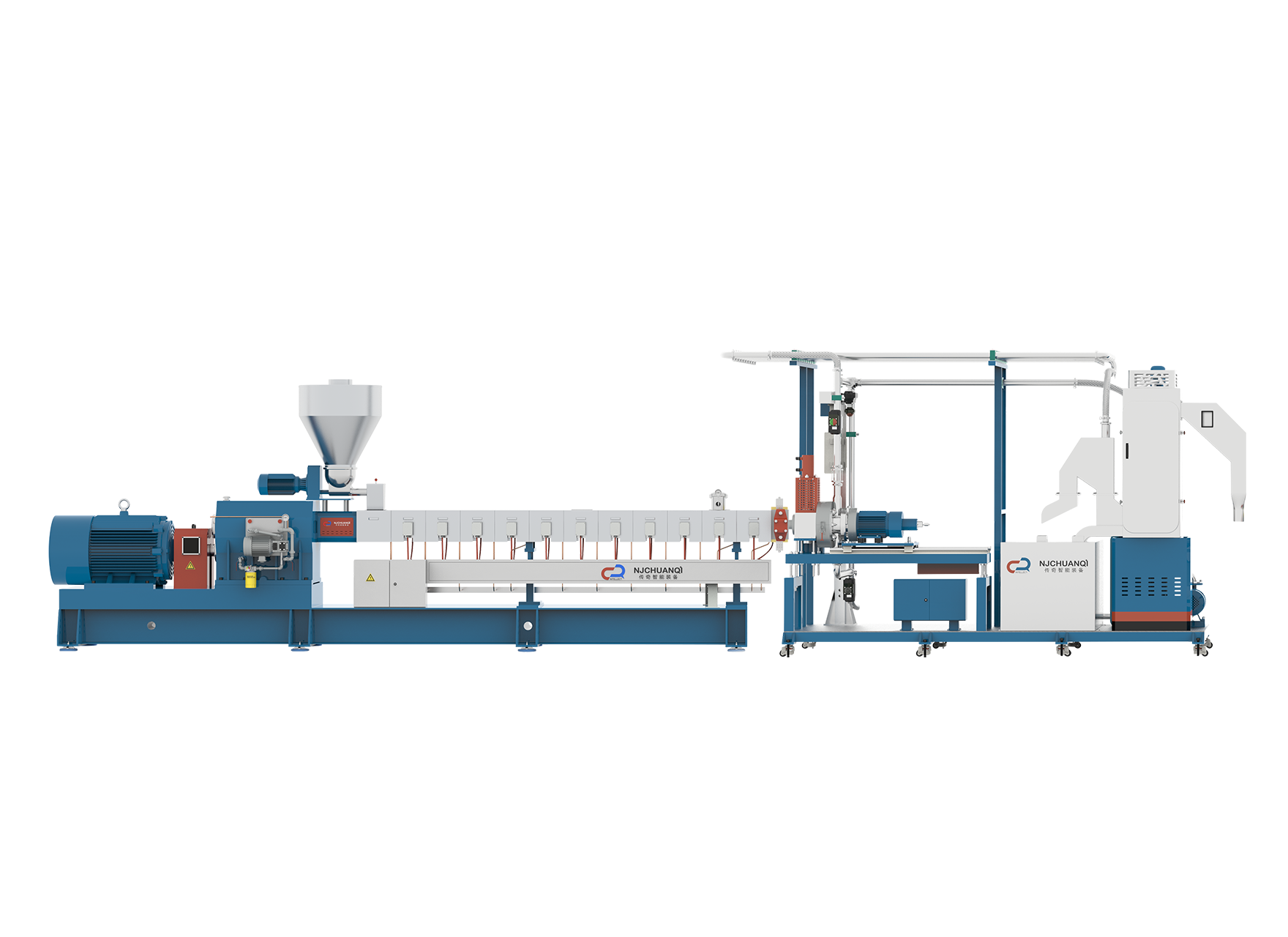
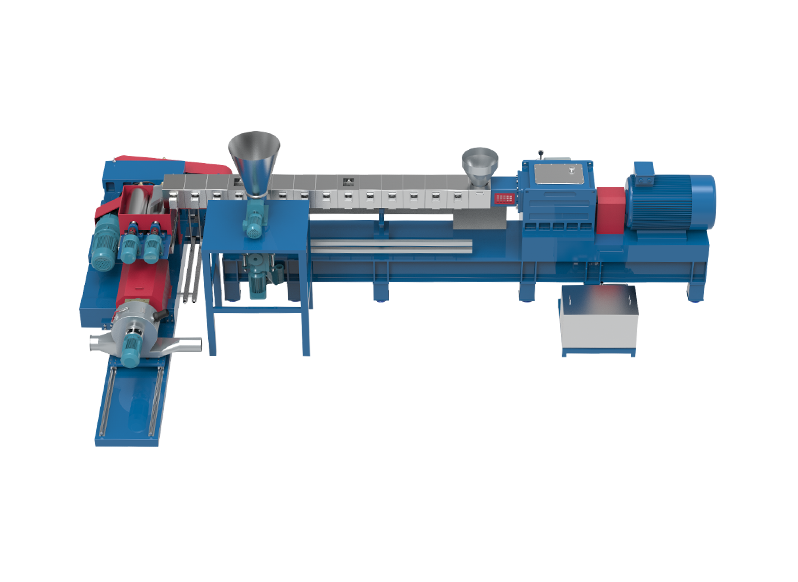
In modern manufacturing environments, the integration of automation and digital monitoring is transforming how equipment like the Polyethylene Extruder Machine operates. Traditionally reliant on manual operation and close on-site supervision, these machines are increasingly being enhanced with automated systems and remote access technologies. This shift has brought notable improvements in production efficiency, process stability, and operational flexibility. This article explores the current capabilities of a Polyethylene Extruder Machine regarding automation and remote monitoring and evaluates how these technologies are being implemented in real-world applications.
Automated Control Systems and Their Impact on Efficiency
One of the significant advancements in extrusion technology is the development of fully automated control systems. These systems allow a Polyethylene Extruder Machine to manage key parameters such as barrel temperature, screw speed, motor torque, die pressure, and material feed rate without requiring constant manual adjustment. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), combined with intuitive Human Machine Interface (HMI) panels, enable operators to pre-set production recipes, monitor trends, and make real-time changes as needed. With automation in place, manufacturers benefit from reduced error rates, consistent product quality, and the ability to run the machine for extended periods with minimal human intervention. Start-up and shutdown sequences can also be automated, reducing waste and setup time between production runs.
Benefits of Automation and Remote Access in Extrusion
The advantages of combining automation with remote access are considerable, especially for operations that demand high throughput and reliability. Automated processes improve production repeatability and reduce the need for skilled operators to monitor every step manually. Remote monitoring enhances machine uptime by allowing quick responses to anomalies and optimizing maintenance schedules based on data-driven insights. Together, these capabilities reduce operational costs, enhance safety, and support scalability for growing production demands. For global manufacturers, remote access also allows centralized oversight of multiple extrusion lines across different facilities, promoting consistent quality and streamlined decision-making.
Implementation Considerations and System Requirements
Despite the clear benefits, integrating automation and remote monitoring into a Polyethylene Extruder Machine requires thoughtful implementation. The machine must be equipped with compatible hardware, such as sensors, actuators, and communication modules. Reliable internet connectivity, secure network protocols, and properly configured software interfaces are essential to protect data integrity and system stability. It is also important to train operators and maintenance personnel to understand and utilize the new technology effectively. Retrofitting older machines with these features is possible but may involve significant investment in hardware and control system upgrades. For new installations, many equipment manufacturers offer pre-configured automation packages with remote access as standard or optional features.
Conclusion: Embracing Smart Extrusion for the Future
In conclusion, the Polyethylene Extruder Machine is increasingly capable of supporting automated operation and remote monitoring, thanks to advancements in control systems, IIoT technology, and smart manufacturing practices. These capabilities not only enhance operational efficiency and product quality but also enable proactive maintenance and greater process transparency. While full integration requires investment and planning, the long-term benefits of automation and remote access make them valuable tools in modern extrusion production. As the industry continues to evolve, these smart features are becoming less of an option and more of a necessity for competitive and sustainable operations.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى +86-189 1339 2785
+86-189 1339 2785