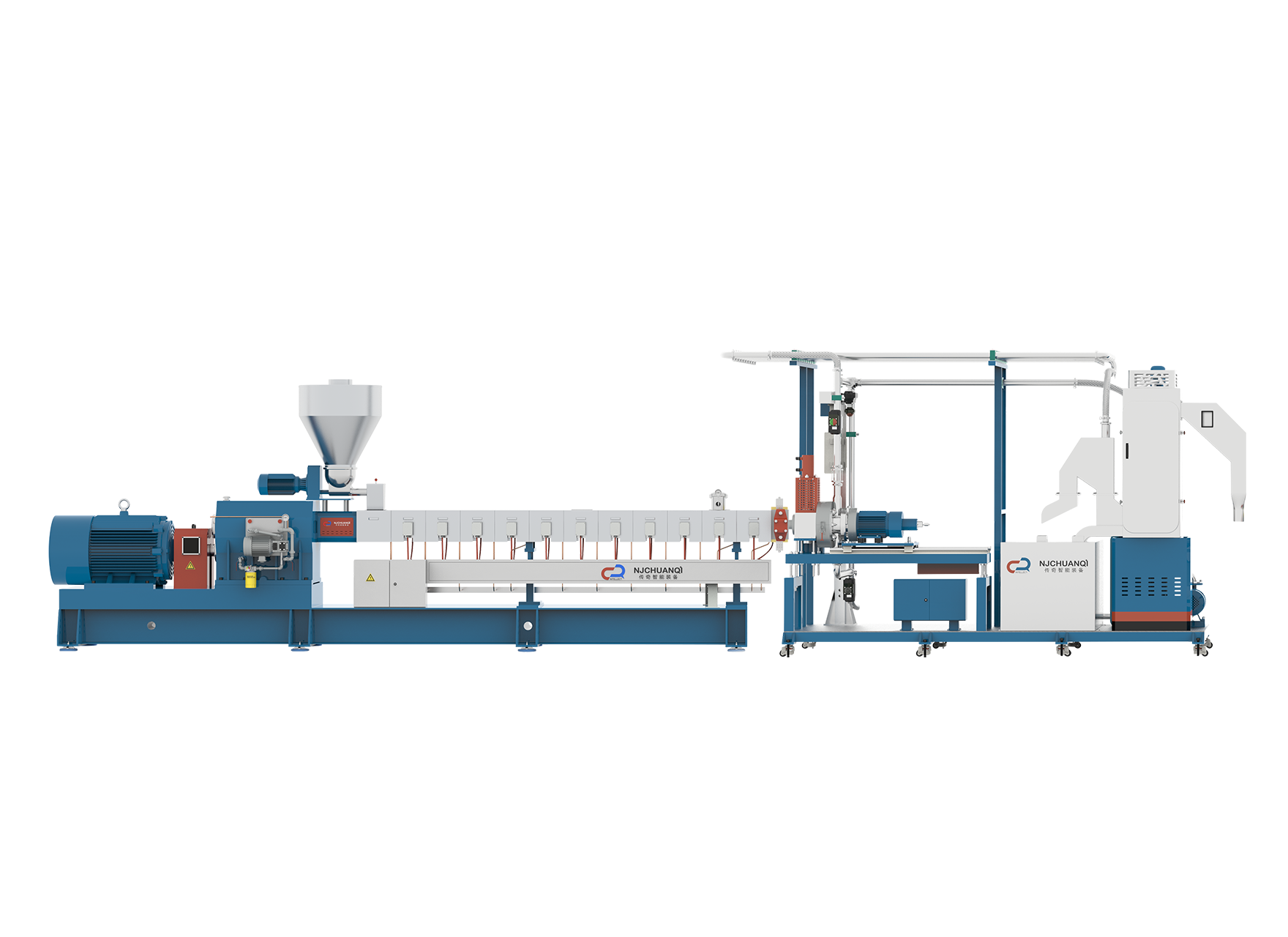
Reactive extrusion is a highly effective process used in polymer blending and modification, allowing chemical reactions to occur during the extrusion process. This technique is invaluable for creating advanced materials with enhanced properties, such as improved strength, thermal stability, or specific functional characteristics. Small scale plastic extruders and twin screw plastic extruders are two types of equipment that play a significant role in enabling reactive extrusion, each offering distinct benefits depending on the application and scale of production.
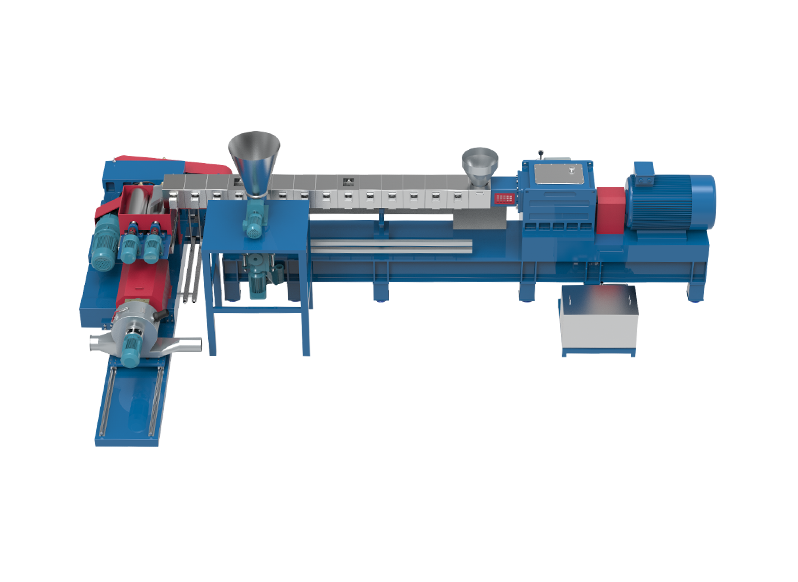
The Role of Reactive Extrusion in Polymer Modification
Reactive extrusion combines polymer blending with chemical reactions to produce materials with customized characteristics. This process often involves adding reactive agents, such as crosslinking agents, compatibilizers, or curing agents, into the polymer during extrusion. The extruder’s temperature, shear, and mixing capabilities allow these agents to interact with the polymer matrix, causing modifications that improve properties such as elasticity, durability, or resistance to heat and chemicals.
Small-Scale Plastic Extruder for Laboratory and Prototype Production
Small-scale plastic extruders are widely used in laboratories and research settings to explore polymer modifications at a smaller, more manageable scale. These machines are often the go-to choice for initial trials or product development phases, where only small batches of material are needed. Small scale extruders provide precise control over the processing conditions, including temperature, screw speed, and pressure. This flexibility allows researchers to fine-tune reaction parameters, making them ideal for experimenting with different combinations of polymers and reactive agents. Despite their smaller size, these machines can still achieve high-quality reactive extrusion, providing valuable insights into material performance before scaling up to industrial production.
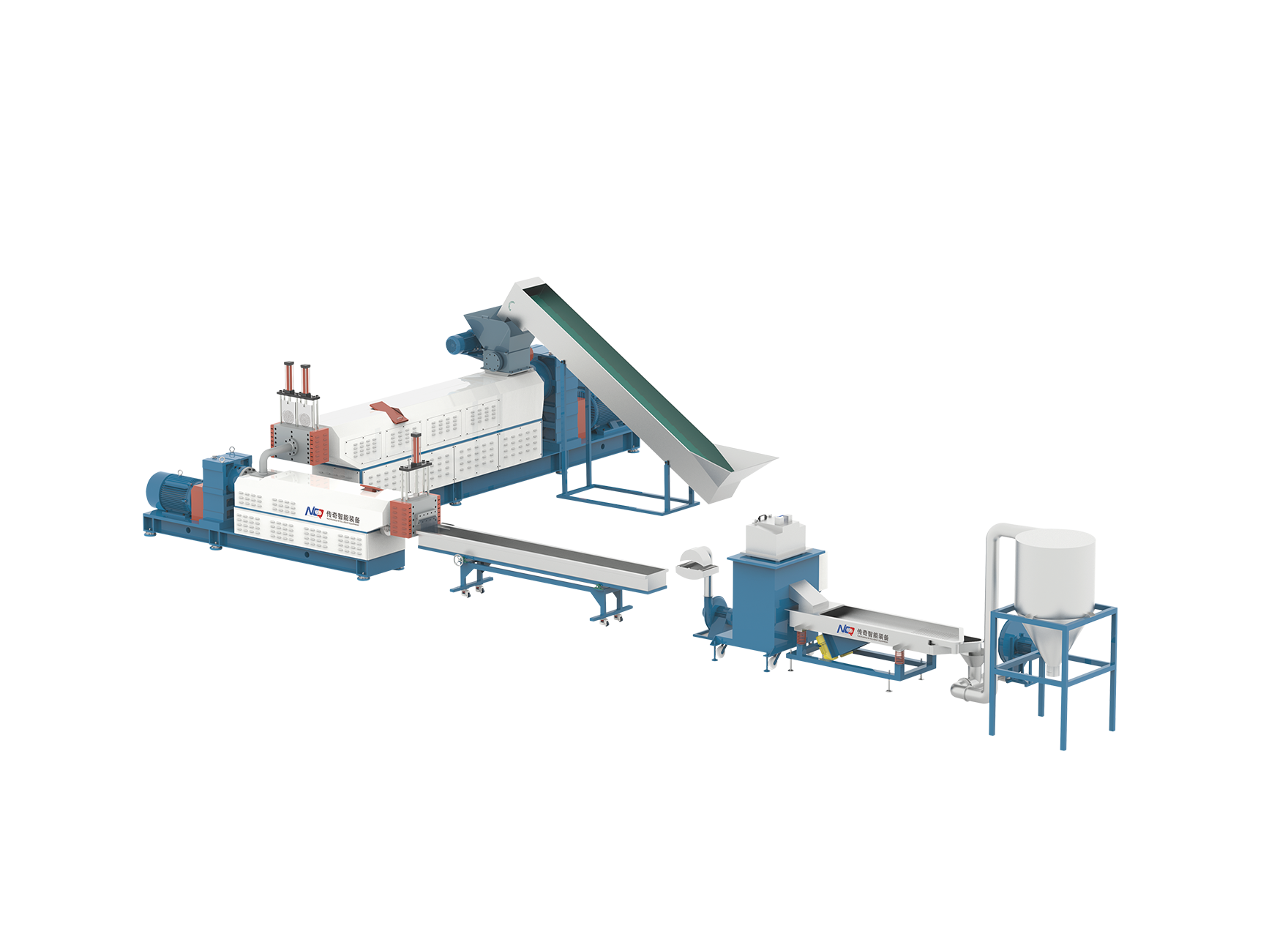
Twin Screw Plastic Extruder for Enhanced Mixing and Reactivity
For more complex polymer modifications or larger scale production, the twin screw plastic extruder is the ideal solution. This type of extruder features two intermeshing screws that rotate in opposite directions, providing good mixing and more effective dispersion of reactive agents throughout the polymer. The twin screw design ensures better control over shear, heat, and residence time, all of which are essential for effective reactive extrusion. The ability to fine-tune these variables allows for more consistent reactions and more uniform material properties, particularly when handling difficult-to-process polymers or when incorporating multiple additives at different stages of the process.
Benefits of Reactive Extrusion with Twin Screw Systems
The key advantage of using a twin screw plastic extruder in reactive extrusion is its good mixing capability. The intermeshing screw design allows for intense mechanical shearing and thorough mixing, which promotes better distribution of additives and ensures a consistent reaction across the entire polymer melt. This is especially crucial in processes like grafting, crosslinking, or incorporating functional fillers, where even dispersion and control of chemical reactions are vital for achieving the desired material properties. Additionally, twin screw systems offer multiple zones for precise temperature control, ensuring that sensitive materials are processed without degradation while still achieving the necessary chemical reactions.
Conclusion
Both small scale plastic extruders and twin screw plastic extruders are essential tools in reactive extrusion processes, enabling polymer modification and blending to achieve advanced material properties. While small scale extruders are good for research and small batch production, twin screw extruders provide the enhanced mixing and reaction control needed for large-scale industrial applications. Together, these machines contribute to the development of custom polymers with improved performance characteristics, helping industries across various sectors meet evolving material demands.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى +86-189 1339 2785
+86-189 1339 2785