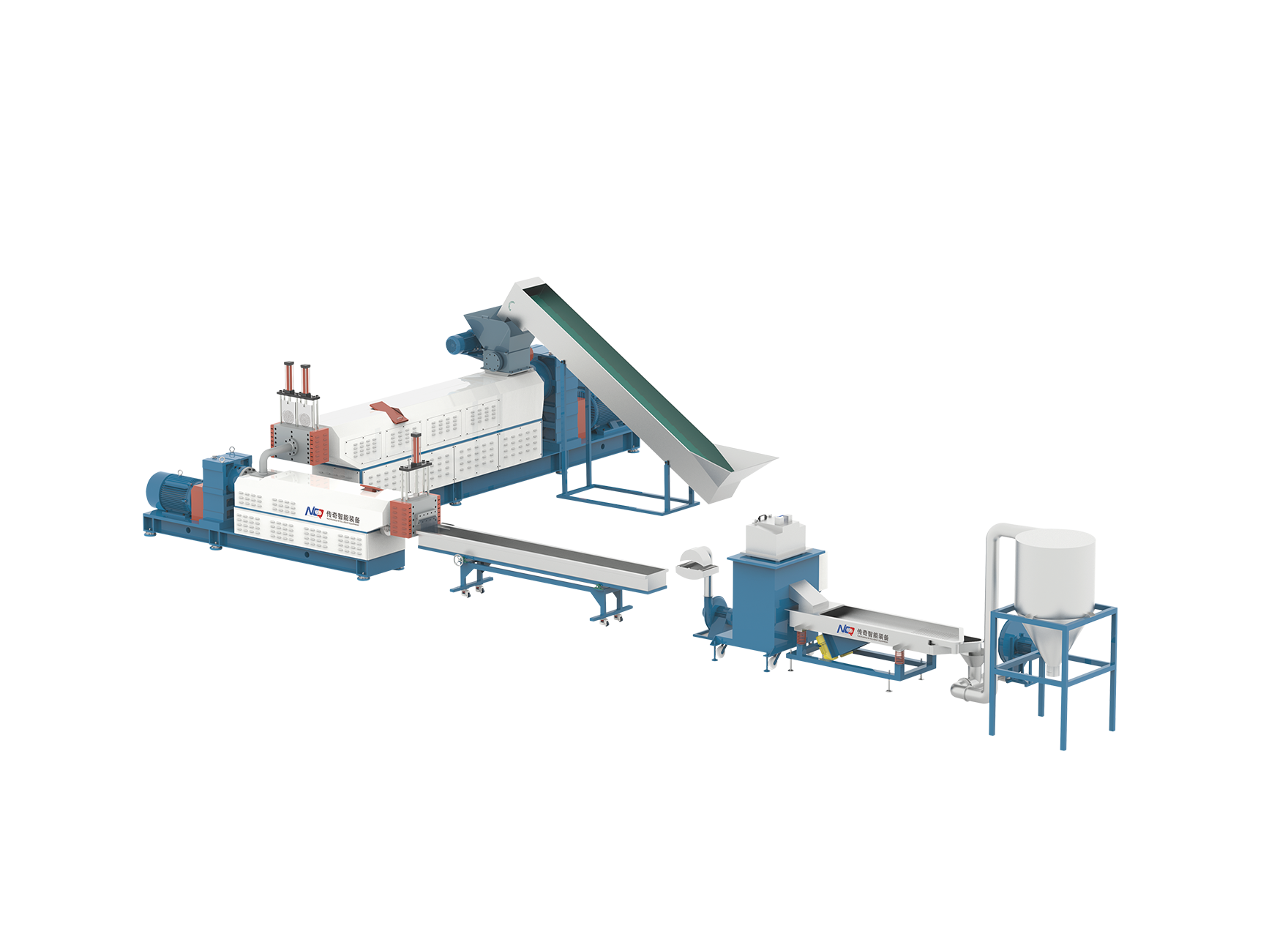
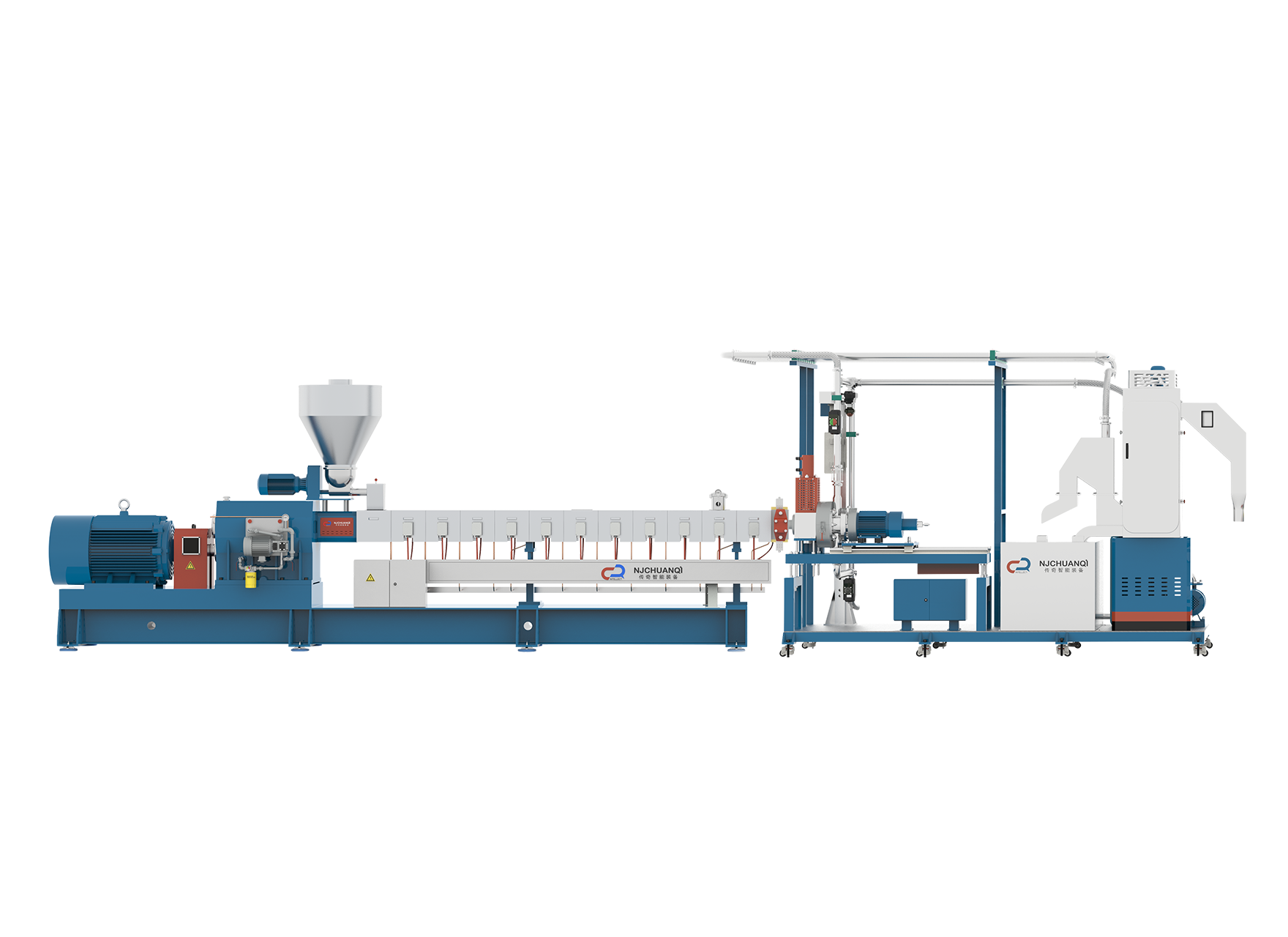
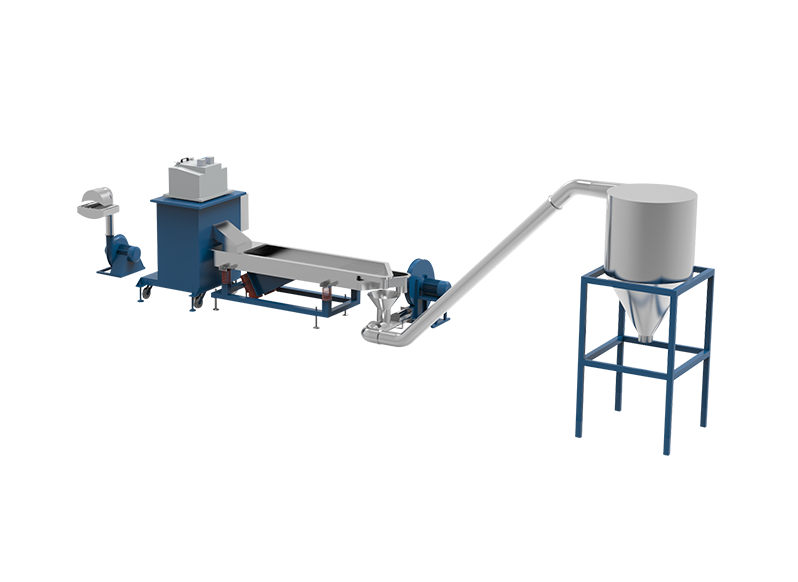
As the world faces mounting plastic waste and growing demand for sustainable manufacturing, converting recycled plastic into usable products has become more urgent and valuable than ever. Extrusion technology plays a central role in this transformation, enabling discarded plastic to be reshaped into functional materials. Two key solutions used in this field are the conventional polymer extruder machine and the more compact, accessible Plasticpreneur extruder. Each offers unique strengths in addressing the technical and environmental challenges of recycled plastic processing.
Consistent Output Despite Variable Input
Recycled plastics come with inherent inconsistencies—differences in polymer type, contamination, and degradation levels make processing more complex than working with virgin material. A polymer extruder machine is typically designed with robust screw configurations and advanced temperature control systems, ensuring reliable melting and mixing even when feedstock quality varies. Similarly, the Plasticpreneur extruder, though smaller in scale, is engineered to deliver steady performance using modular components and carefully optimized heating elements. Both machines allow operators to maintain consistent extrusion output, a critical requirement for producing uniform products like filaments, beams, or plastic sheets.
Adaptability Across Different Plastic Types
Effective recycling depends on flexibility. Whether dealing with HDPE from detergent bottles, LDPE from plastic bags, or shredded PP from packaging, an extruder must adapt to different melt flow behaviors. These systems often support adjustable parameters like screw speed, feed rate, and die shape. The Plasticpreneur model, in particular, is designed to switch quickly between different plastic types without needing extensive cleaning or recalibration. This is especially advantageous in decentralized or small-scale recycling hubs, where the plastic feedstock may change daily.
Lower Material Waste and Energy Use
Both types of extruders are optimized for energy efficiency and low-waste operation. For example, small-batch processing on the Plasticpreneur extruder reduces the material required for setup and testing, making it ideal for prototyping or educational environments. Polymer extruder machines, while larger, are often equipped with multi-zone heating and advanced motor systems to reduce energy consumption during continuous operation. These characteristics help reduce the environmental footprint of recycling processes and improve overall material yield.
Democratizing Plastic Recycling
While industrial extruders serve manufacturing plants, the Plasticpreneur extruder is explicitly designed for accessibility. Its affordability, modularity, and user-friendly design allow individuals, startups, and community workshops to participate in the circular economy. This democratization is vital—bringing plastic recycling into classrooms, rural communities, and micro-factories expands local capacity for waste reduction and product innovation. In this way, extrusion becomes not only a technical process but also a social tool for environmental empowerment.
Supporting Closed-Loop Circular Systems
Ultimately, both machines contribute to the broader goal of closed-loop recycling. By converting post-consumer plastic into new products that can themselves be recycled, these extruders reduce the demand for virgin plastic and keep materials in circulation longer. Whether producing recycled building materials, 3D printing filament, or handcrafted goods, extrusion provides the mechanical foundation for scalable and sustainable plastic reuse. The combination of precision, adaptability, and efficiency ensures that recycled plastic can be processed into high-quality, durable, and functional products.
Conclusion
Processing recycled plastic requires more than just good intentions—it demands reliable, flexible, and efficient machinery. Whether through the industrial-grade capabilities of a polymer extruder machine or the accessible design of a Plasticpreneur extruder, both technologies play a vital role in enabling plastic recycling to move from concept to practice. As materials science, design thinking, and environmental stewardship converge, extrusion will remain a cornerstone in building a truly circular plastic economy.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى +86-189 1339 2785
+86-189 1339 2785