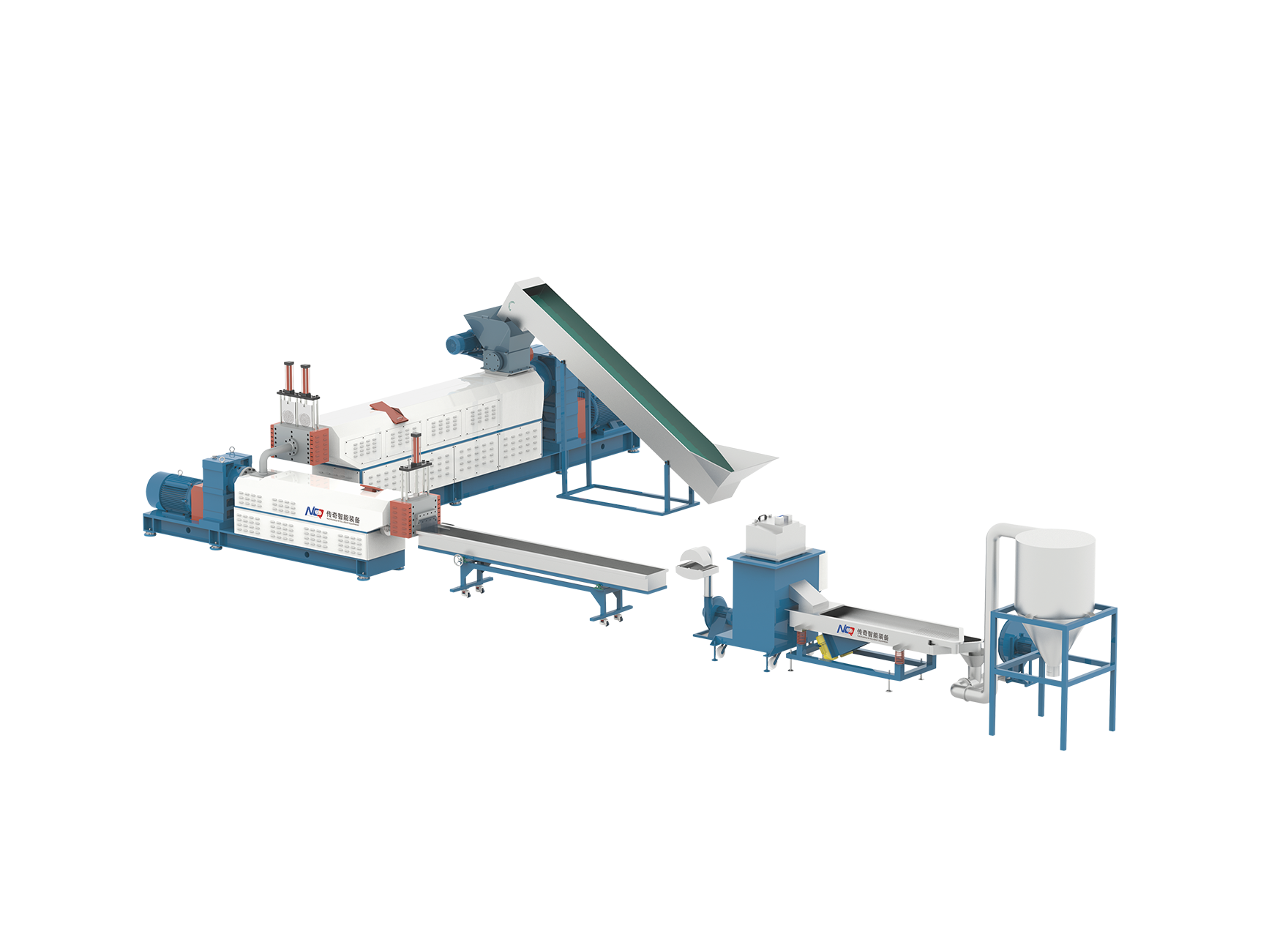
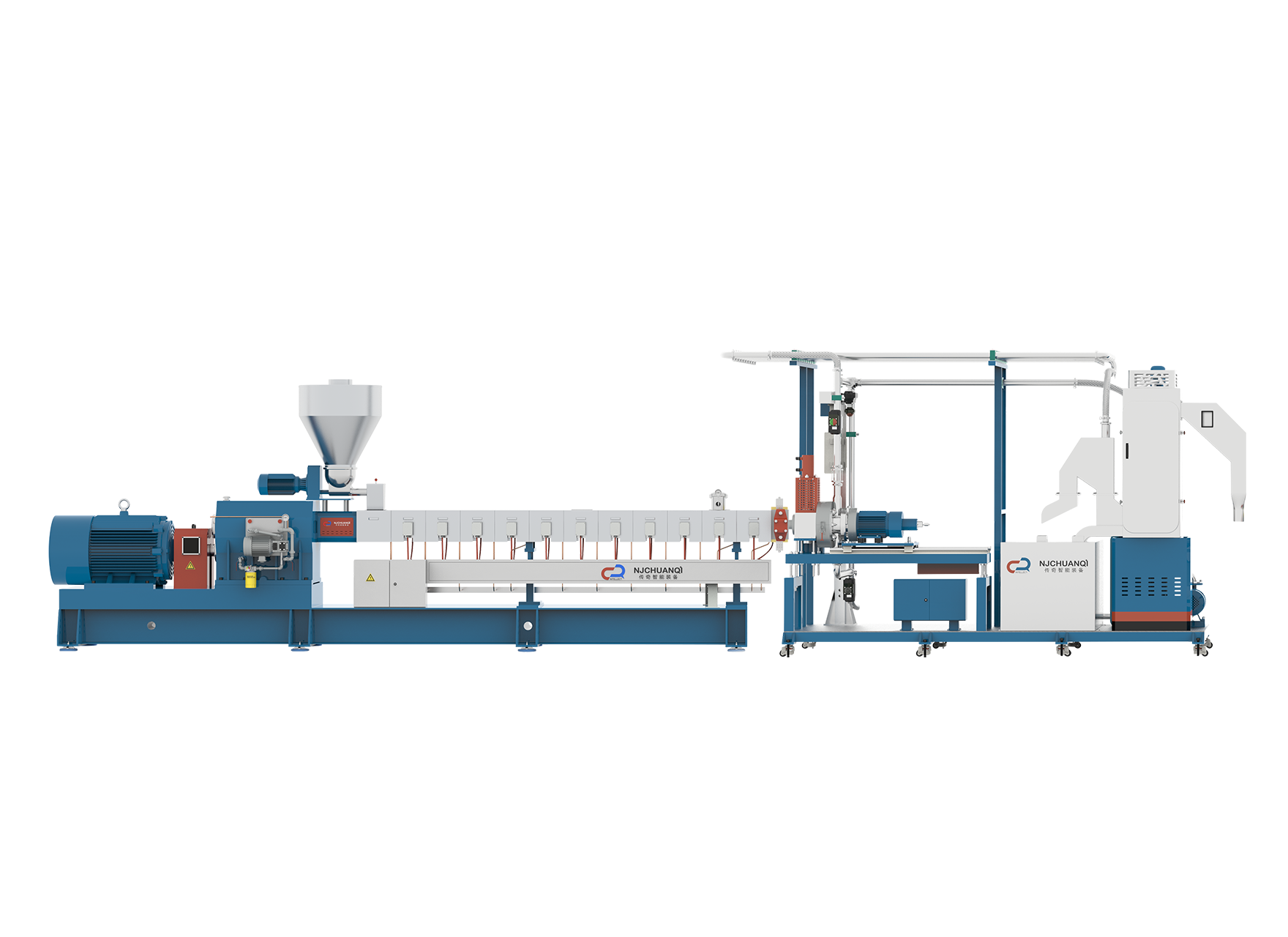
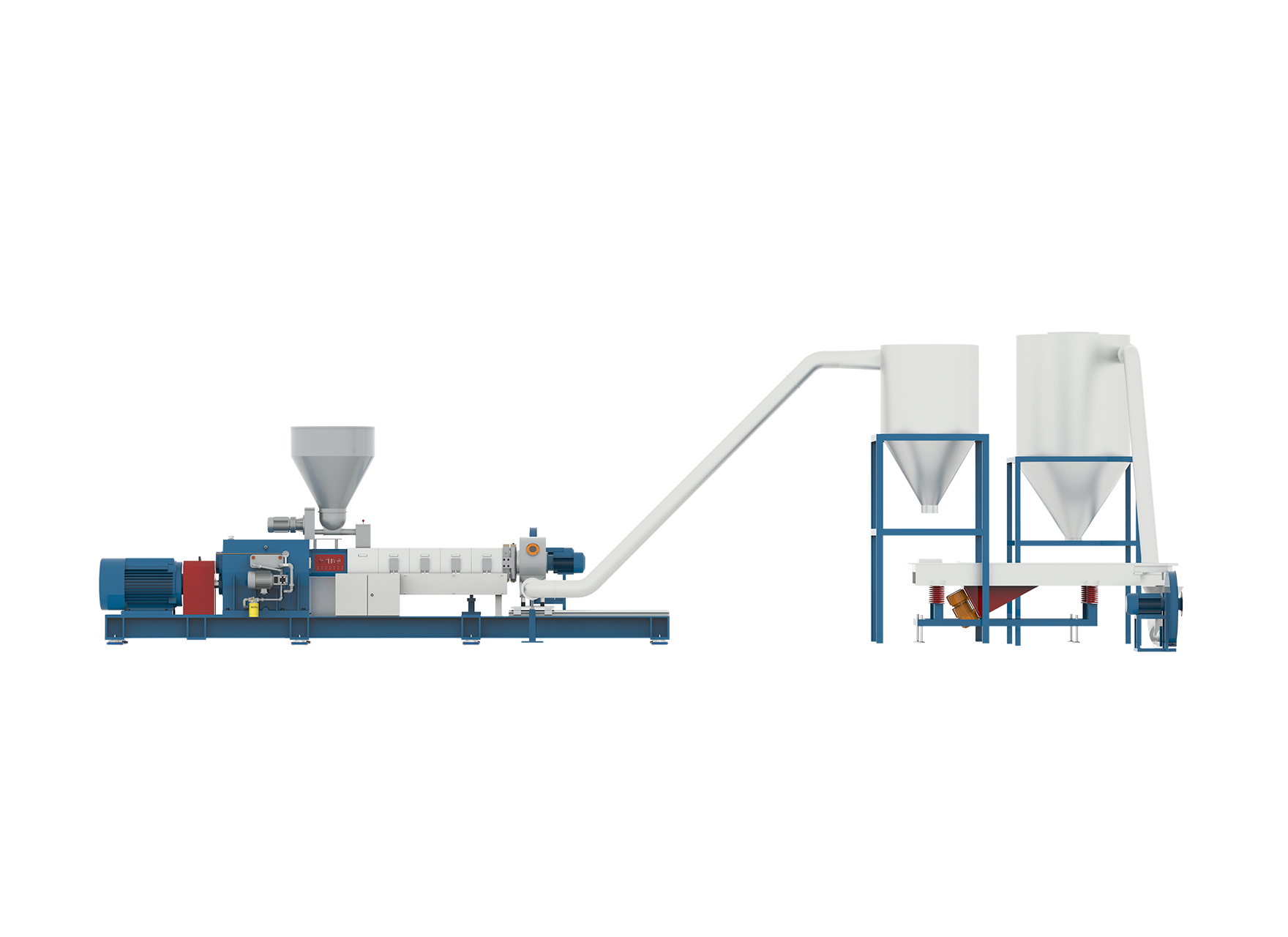
Noise level is an important consideration in laboratory equipment, especially for devices like lab scale extruders used in research and small-scale production. Among the popular types are the Lab Scale Twin Screw Extruder and the Lab Scale Single Screw Extruder. Understanding their noise characteristics can help users choose the right equipment to maintain a safer and more comfortable working environment without compromising performance.
Factors Influencing Noise in Lab Scale Extruders
The noise generated by extruders primarily comes from mechanical components such as motors, gearboxes, screws, and bearings, as well as from the material processing itself, including melting and conveying. The design and configuration of the extruder strongly affect these noise levels.
Twin screw extruders typically have two intermeshing screws rotating simultaneously, which can cause more mechanical complexity and potential noise sources compared to single screw extruders. However, advanced engineering and sound insulation can mitigate much of this noise.
Noise Characteristics of Lab Scale Twin Screw Extruders
Lab Scale Twin Screw Extruders are favored for their good mixing and processing capabilities, especially for complex or multi-component materials. However, the engagement of two screws and their synchronized rotation may introduce higher mechanical noise due to the interaction between screws and increased number of moving parts.
The motors powering twin screw extruders are usually designed to handle higher torque, which can also contribute to noise. Yet, manufacturers often incorporate vibration-damping materials, precision bearings, and optimized gearboxes to reduce operational noise.
Additionally, since twin screw extruders often operate at varying speeds depending on the application, noise levels may fluctuate. At lower speeds, noise tends to be quieter, while higher speeds may generate more audible sound due to increased mechanical activity and material shear.
Lab Scale Single Screw Extruders, in contrast, generally produce less mechanical noise due to their simpler design. With only one rotating screw, there are fewer moving components interacting, causing reduced vibration and sound emissions.
The motor and drive systems for single screw extruders tend to be smaller and less complex, which typically results in quieter operation. However, single screw extruders may produce some noise from the material melting and conveying process, but this is usually less pronounced.
Applications that do not require extensive mixing or compounding often prefer single screw extruders due to their quieter operation and simpler maintenance.
Comparison and Considerations for Laboratory Settings
When noise is a critical factor in laboratory environments, single screw extruders may be advantageous due to their inherently lower mechanical noise. However, if processing complexity demands a twin screw extruder, selecting models with noise reduction features and implementing external soundproofing can help manage sound levels.
Operators should also consider the placement of the extruder in rooms with adequate acoustic treatments and the use of personal protective equipment if necessary. Regular maintenance ensures that bearings and gears remain lubricated and aligned, preventing excess noise caused by wear or damage.
Noise level measurements, often expressed in decibels (dB), vary between different extruder models and brands. Prospective users should request noise specifications and, if possible, observe operational demonstrations to assess suitability.
Conclusion
Both Lab Scale Twin Screw Extruders and Lab Scale Single Screw Extruders have distinct noise profiles influenced by their mechanical designs and operating conditions. While twin screw extruders may generate higher noise due to their complexity, modern engineering solutions can effectively reduce this. Single screw extruders generally offer quieter operation and are suitable for less demanding processes.
Understanding these differences allows laboratory managers and researchers to select extruder equipment that balances processing needs with noise considerations, promoting a productive and comfortable working environment.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى +86-189 1339 2785
+86-189 1339 2785